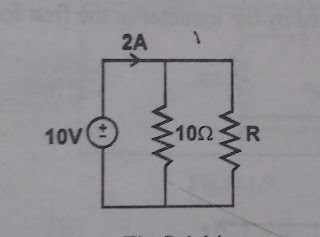
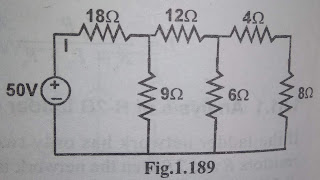
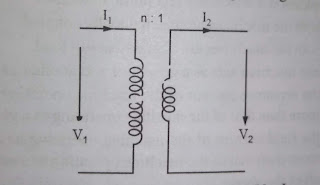
What is Resistance ?
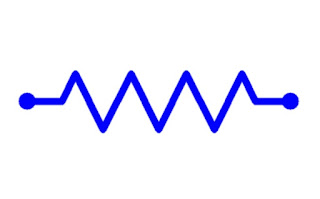
Resistor is a fundamental passive element. The resistor is a circuit component whose principle property is to oppose the flow of current through it . Resistance is represented by the letter "R". The symbol of the resistance is shown in below figure. Units for resistance is shown in below figure A conductor is said to have resistance of 1 ohm , if it permits one Ampere of current to flow through it when 1 Volt is applied across it's terminals. For conductors such as metals ,the resistance is very low . This is due to the presence of free electrons in their atoms. For insulators the resistance is very high and for semiconductors the resistance lies in between that of metal and insulator. The resistance R of a conductor depends on the following factors . 1) It is directly proportional to length of the conductor 2) It is inversely proportional to area of cross section of t